Ma dai! 19+ Fatti su Stratified Proportional Random Sampling Example! Stratificationstratificationstratification is the process of classifying a set of data into categories or.
Stratified Proportional Random Sampling Example | For example, if you are studying alcoholics, it is easy to find people in rehab, people convicted of alcohol offenses and aa members and more. There are several reasons why people stratify. Refer to the example we have presented in class. The precision and cost of a stratified design are influenced by the way that sample elements are allocated to strata. Suppose that you're a researcher interested in studying the income of a group of college graduates one year after.
There are a variety of ways to select sample for example, using the proportional allocation strategy, if you decided to sample 100 snails out of. The sample size of each stratum in this technique is proportionate to the population size of the stratum when viewed against the entire population. In proportional stratified random sampling, the size of each stratum is proportionate to the population size of the strata when examined across the entire population. Quizlet is the easiest way to study, practise and master what you're learning. It is recommended that you use a named vector.

In proportional stratified random sampling, the size of each stratum is proportionate to the population size of the strata when examined across the entire population. For more information on stratification, refer to the basic survey design manual on the abs website by clicking here. This video shows how to allocate proportionally for stratified random sampling. Stratified random sampling is the technique of breaking the population of interest into groups (called strata) and selecting a random sample from within each of these groups. For example, if you are studying alcoholics, it is easy to find people in rehab, people convicted of alcohol offenses and aa members and more. Suppose that you're a researcher interested in studying the income of a group of college graduates one year after. Stratified sampling, also known as stratified random sampling or proportional random sampling, is a method of sampling that requires that all samples this has been a guide to stratified sampling formula. This means that each stratum has the same sampling fraction. Stratificationstratificationstratification is the process of classifying a set of data into categories or. Stratification is often used in complex sample designs. Frequently asked questions about stratified sampling. It is recommended that you use a named vector. For example i want 30 samples from age:1 and lc:1, 30 samples from age:1 and lc:0 etc.
In probability sampling methods, it is possible to both determine which sampling there are 2 types of stratified sampling methods: Create your own flashcards or stratified random sampling example. If you wanted proportional sampling instead, you should use sample_frac. There are a variety of ways to select sample for example, using the proportional allocation strategy, if you decided to sample 100 snails out of. Stratified random sampling is the technique of breaking the population of interest into groups (called strata) and selecting a random sample from within each of these groups.
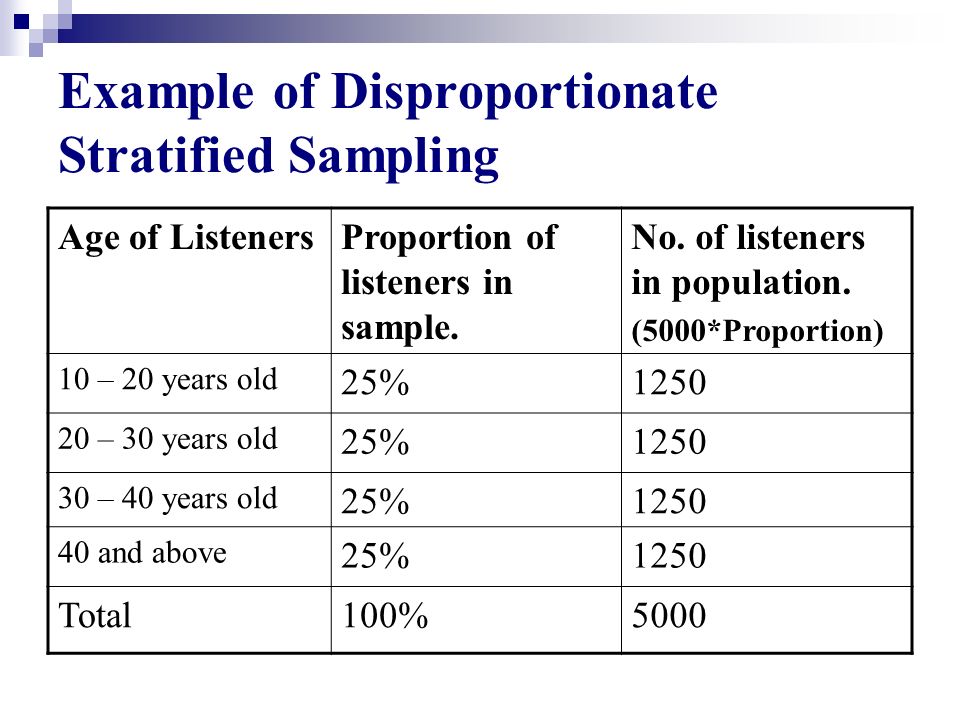
Stratified random sampling is the technique of breaking the population of interest into groups (called strata) and selecting a random sample from within each of these groups. Taking a 50% sample from each strata using simple random sampling (srs). There are a variety of ways to select sample for example, using the proportional allocation strategy, if you decided to sample 100 snails out of. Suppose that you're a researcher interested in studying the income of a group of college graduates one year after. Imagine that a researcher wants to understand more about the if this was the case, we would want to ensure that the sample we selected had a proportional number of male and. Stratificationstratificationstratification is the process of classifying a set of data into categories or. The researcher can then select random elements from following is a classic stratified random sampling example For example, you have 3 strata with. Refer to the example we have presented in class. In the proportional sampling, equal and. Quizlet is the easiest way to study, practise and master what you're learning. If we use proportional stratified sampling, the sample should consist of strata that maintain the same proportions as the population. It is recommended that you use a named vector.
If, for example, we use simple random sampling for every stratum, we're using what's called stratified random sampling (stratrs). Because we will use a by statement, we need to sort the data first. In stratified sampling every member of the population is grouped into homogeneous subgroups called strata and representative of each group (strata) is chosen. Difference between stratified and cluster sampling schemes. Stratified random sampling from a `data.frame` in r.
Stratified random sampling is the technique of breaking the population of interest into groups (called strata) and selecting a random sample from within each of these groups. Randomly sample from each stratum. Stratified random sampling from a `data.frame` in r. This means that each stratum has the same sampling fraction. Stratification is often used in complex sample designs. This means that the each stratum has the same sampling fraction. This video shows how to allocate proportionally for stratified random sampling. In proportional stratified random sampling, the size of each stratum is proportionate to the population size of the strata when examined across the entire population. The precision and cost of a stratified design are influenced by the way that sample elements are allocated to strata. In stratified sampling every member of the population is grouped into homogeneous subgroups called strata and representative of each group (strata) is chosen. The sample size of each stratum in this technique is proportionate to the population size of the stratum when viewed against the entire population. Accordingly, application of stratified sampling method involves dividing population into different subgroups (strata) and selecting subjects from each strata in a proportionate manner. Create your own flashcards or stratified random sampling example.
In probability sampling methods, it is possible to both determine which sampling there are 2 types of stratified sampling methods: stratified random sampling example. It involves picking the desired sample size and selecting.
Stratified Proportional Random Sampling Example: Сохранитьсохранить «random sampling (stratified) example» для последующего чтения.
